FCC Chair Proposes New Metric for Accidental Explosions in Space
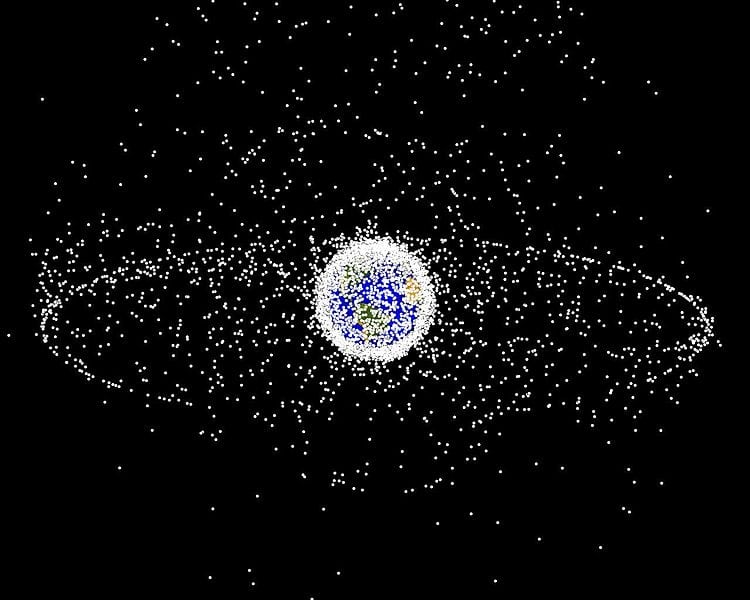
Rendering of projected orbital debris in two primary fields: the ring of objects in geosynchronous orbit (GEO) and the cloud of objects in low Earth orbit (LEO). Photo: Wikimedia Commons
FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel called on the agency this week to update its orbital debris mitigation rules to limit the risks of accidental explosions in space.
Rosenworcel proposes adding a specific, quantitative metric that satellites must meet. If adopted, the updated rules would require satellite applicants to assess and limit the probability of debris-generating accidental explosions to be less than 1 in 1,000 for each satellite.
This metric would “provide satellite operators an objective and transparent benchmark for demonstrating as part of their applications to the Commission that they have assessed and limited the probability of accidental explosions during and after the completion of mission operations,” the FCC Chairwoman’s office said in a press release.
The FCC said that this probability metric is consistent with the U.S. Government Orbital Debris Mitigation Standard Practices. If adopted, it would be phased in one year after publication in the Federal Register.
“We can no longer afford to launch new satellites into our skies without being thoughtful about space sustainability,” Rosenworcel said in a release. “Our orbital debris mitigation efforts will help preserve the orbital environment to protect services we rely on and allow new services to be launched.”
The FCC is working to refresh the record orbital debris mitigation rules. In a public notice published on May 2, the FCC asked for comments to refresh the record on rule changes about orbital debris mitigation. The last full update was in 2020 and the FCC noted there have been a number of changes in the market since then. Comments are due June 27.