Aerojet Rocketdyne Successfully Completes Qualification Tests on Reusable Engine
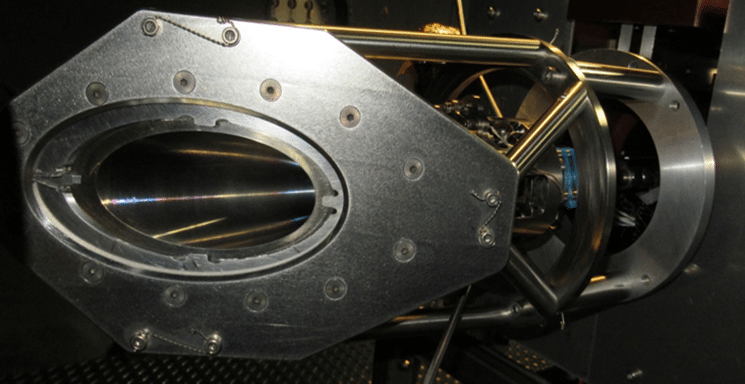
The MR-104J hydrazine monopropellant engine. Photo: Aerojet Rocketdyne
Aerojet Rocketdyne has successfully completed hot-fire qualification tests of an engine that demonstrates the ability to meet reusability requirements for Boeing’s Crew Space Transportation (CST) 100 Starliner crew module propulsion system. The engine tested was Aerojet Rocketdyne’s MR-104J hydrazine monopropellant engine in Redmond, Washington. For NASA service missions to the International Space Station (ISS), Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft will carry up to four astronauts and time-critical scientific research.
The Starliner crew module propulsion system will use 12 MR-104J engines for reaction control to orient the vehicle during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere. Prior to re-entry, Aerojet Rocketdyne’s service module engines will provide attitude control.
Aerojet Rocketdyne designed, developed and tested the MR-104J under the company’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) subcontract to Boeing. Similar to other reaction control system engines, the MR-104J includes additional features to increase redundancy that meet critical requirements and improved strength to withstand multiple shocks at operating temperatures. The engine upgrades also provide reusability for Boeing as it certifies Starliner crew modules for multiple missions.
Under the Boeing CCtCap subcontract, Aerojet Rocketdyne will provide propulsion system hardware that includes crew module reaction control engines; launch abort engines; orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters; and service module reaction control system thrusters. Boeing will assemble propulsion hardware into the Starliner spacecraft at its Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.