NASA-ISRO Satellite’s Antenna Reflector Passes CDR
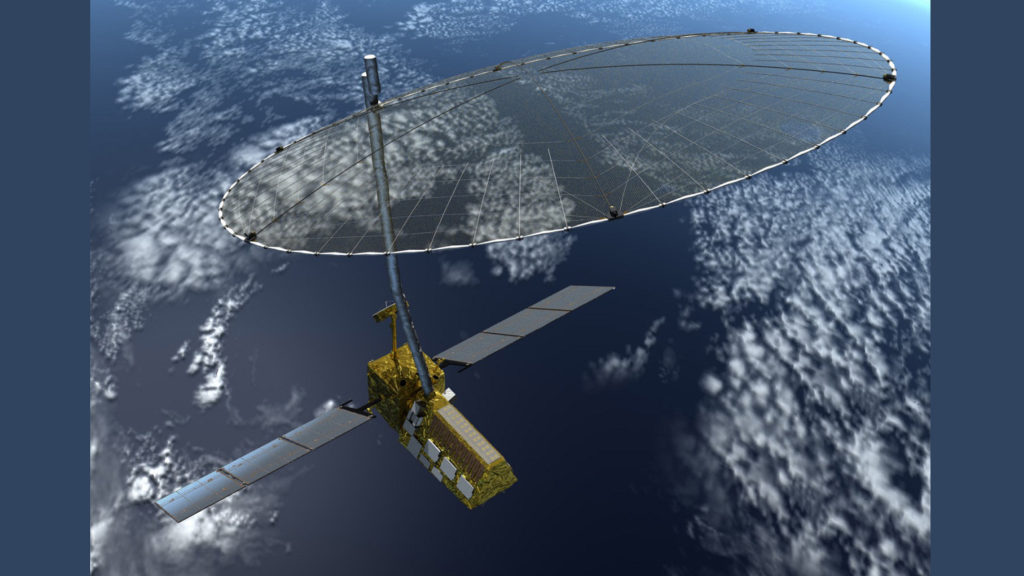
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite. Photo: NASA JPL
Northrop Grumman’s Astro Aerospace has successfully completed a Critical Design Review (CDR) of the AstroMesh radar antenna reflector for the NASA–Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite. NISAR will make global integrated measurements, providing a detailed view of Earth. The radar imaging satellite will use dual L-band and S-band frequencies to measure the causes and consequences of land surface changes.
Post CDR, the program will move into the “build” phase of the AstroMesh radar antenna reflector in preparation for the scheduled 2021 launch date. Northrop Grumman will use its proprietary AstroMesh deployable mesh reflector for NISAR’s large aperture antenna, building an ultralight and extremely stiff reflector suited for high frequency communications and radar applications.
The data collected by the NISAR satellite will provide information to better manage resources and global change. NISAR is a partnership between NASA and the ISRO. NASA’s contribution to NISAR is being managed and implemented by the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California.